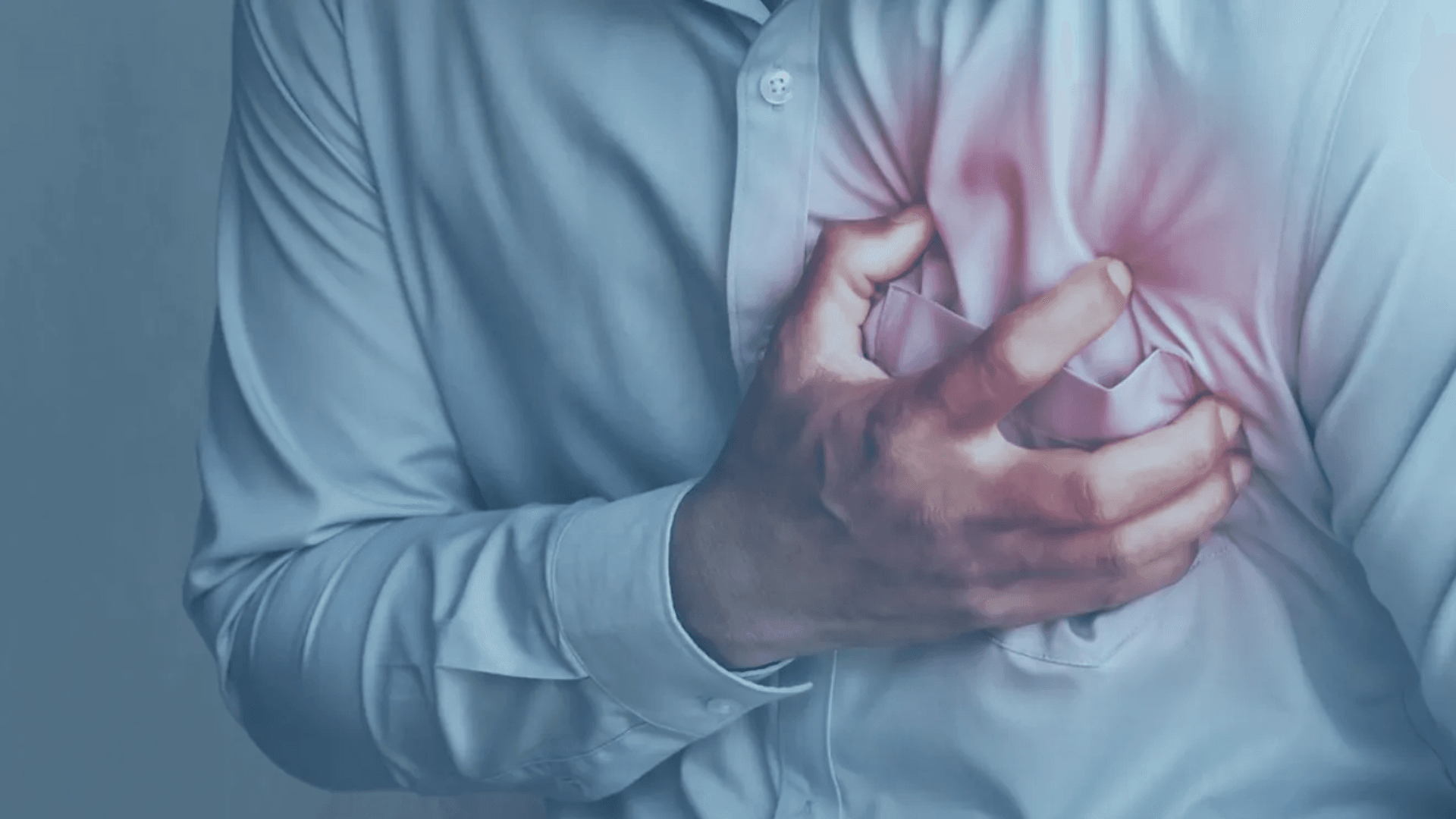
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, usually by a clot in a coronary artery. This event can be fatal if not treated quickly. In this article, we address the causes of heart attack, its symptoms, the available treatments, and the best ways to prevent a heart attack.
What is Myocardial Infarction?
Myocardial infarction happens when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen due to a blockage in the coronary arteries. This blockage can be caused by the buildup of fatty plaques (atherosclerosis) or by a blood clot.Main Causes and Risk Factors
The main risk factors for myocardial infarction include:
✔ High blood pressure: High pressure overloads the heart and damages the arteries. ✔ High cholesterol: Fat buildup in the arteries can lead to atherosclerosis. ✔ Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels. ✔ Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart attack. ✔ Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to fat accumulation in arteries. ✔ Obesity: Excess weight is linked to various cardiac risk factors. ✔ Stress and anxiety: Stress can raise blood pressure and trigger heart problems. ✔ Family history: People with first-degree relatives who have had heart attacks are more prone to the disease.Symptoms of Heart Attack
The symptoms of heart attack can vary, but the most common include:
✔ Chest pain: Feeling of tightness or heaviness in the chest, which may radiate to the left arm, back, jaw, or shoulders. ✔ Shortness of breath: Feeling difficulty breathing even without physical effort. ✔ Excessive sweating: Sudden and intense cold sweat. ✔ Dizziness and fainting: Could be a sign of a sudden drop in blood pressure. ✔ Nausea and vomiting: More common in women. ✔ Extreme fatigue: Feeling unexplained tiredness.The symptoms of heart attack in women can be subtler, such as stomach pain, intense fatigue, and unexplained anxiety.Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction
To confirm a heart attack, doctors perform various tests to detect heart attack, such as:
✔ Electrocardiogram (ECG): Assesses the electrical activity of the heart. ✔ Blood tests: Detect enzymes released when the heart muscle is damaged. ✔ Echocardiogram: Checks the heart’s function. ✔ Coronary angiography: Identifies obstructions in the coronary arteries.Treatment for Heart Attack
Treatment of myocardial infarction depends on the severity of the case and may include:
✔ Use of medications: Such as thrombolytics (to dissolve clots), beta-blockers, aspirin, and statins. ✔ Coronary angioplasty: Procedure to unblock the blocked artery and place a stent. ✔ Coronary artery bypass surgery: Creating a new path for blood to flow around the blockage. ✔ Post-heart attack rehabilitation: Programs to help patients recover and prevent new cardiac events.Attention! Treatment for heart attack should always be done under medical supervision. Self-medication can be extremely dangerous and worsen the condition.Prevention of Heart Attack
The best way to avoid a heart attack is to follow preventive measures. Here are some effective strategies for heart attack prevention:
✔ Maintain a healthy diet: Reduce consumption of saturated fats, sugar, and salt. ✔ Engage in regular physical activity: Aerobic exercises strengthen the heart. ✔ Manage stress: Techniques like meditation and yoga help reduce blood pressure. ✔ Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. ✔ Regularly monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar. ✔ Periodically consult a cardiologist for preventive check-ups.Conclusion
Myocardial infarction is one of the leading causes of death worldwide but can be prevented with healthy habits and regular medical follow-up. Recognizing heart attack symptoms quickly and seeking medical help can save lives.
If you have risk factors or a family history of heart disease, don’t wait for symptoms to appear. Consult a doctor and take care of your cardiovascular health!