Acne is a very common skin condition, affecting millions of people worldwide. Although it is more frequent during adolescence, it can persist into adulthood and impact the self-esteem of those who suffer from it. In this article, we explore the main causes, types of acne, available treatments, and the best ways to prevent it.
What is Acne?
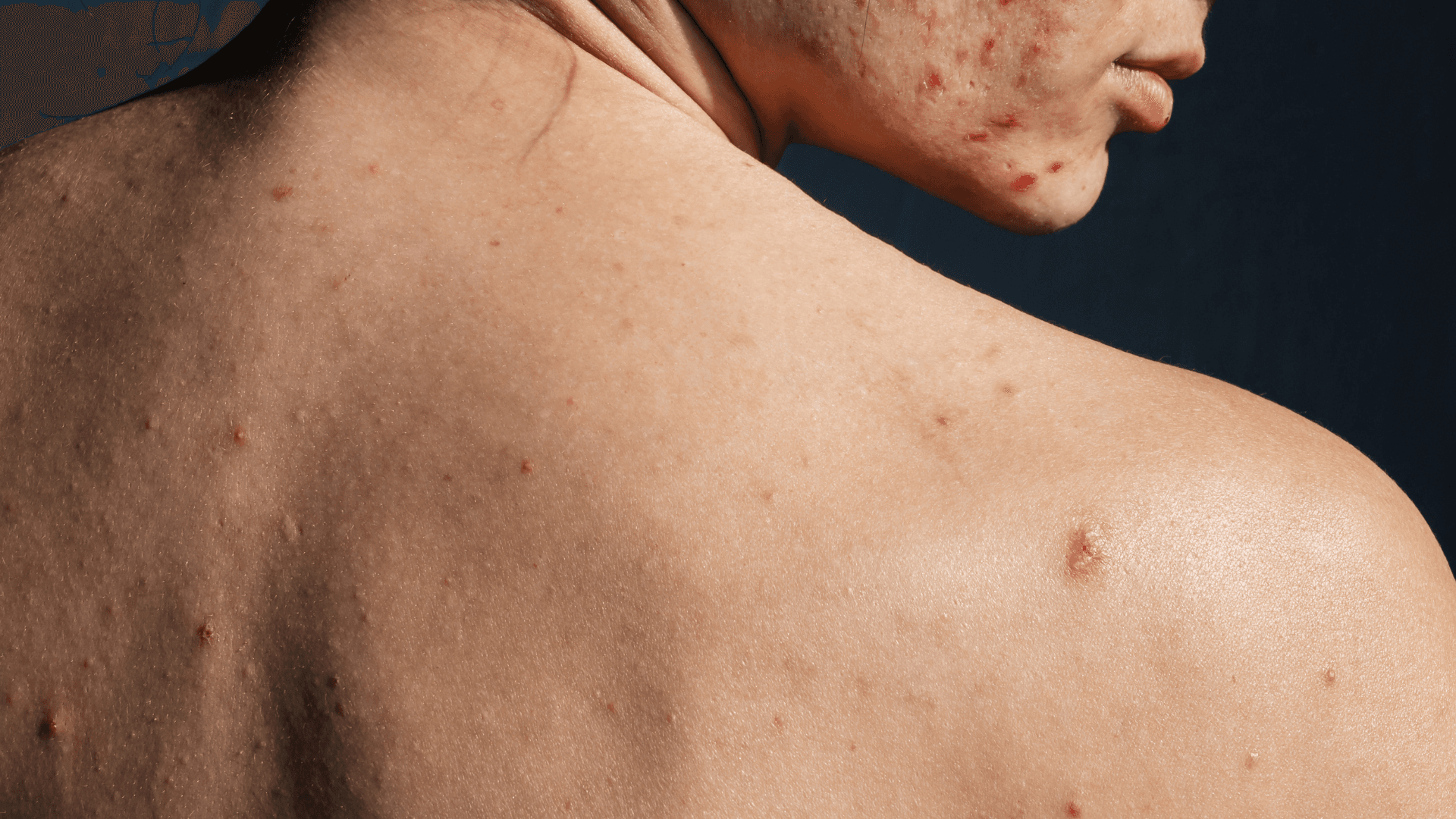
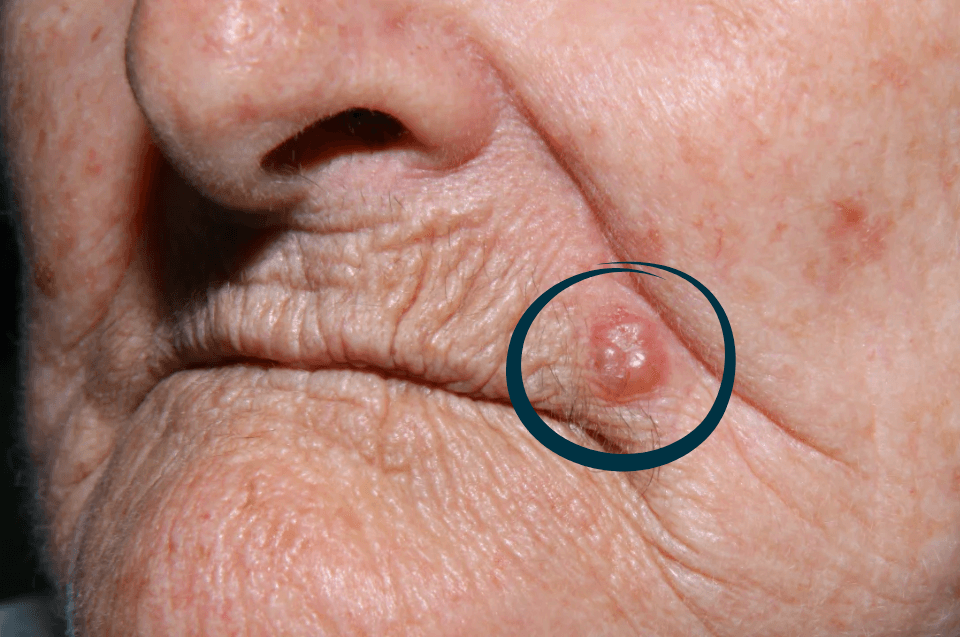
Acne is an inflammatory skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with sebum and dead cells. This leads to the appearance of blackheads, pimples, and in more severe cases, painful nodules and cysts. Acne can appear on the face, back, shoulders, and chest, being influenced by hormonal, genetic, and environmental factors.Main Causes of Acne
Several factors contribute to the development of acne, including:- Excessive sebum production: Overactive sebaceous glands increase skin oiliness, favoring the emergence of pimples.
- Accumulation of dead cells: When cellular renewal is inefficient, pores can become clogged.
- Proliferation of the bacterium Propionibacterium acnes: This bacterium can trigger inflammation in blocked follicles.
- Hormonal factors: Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy can stimulate sebum production.
- Stress: Stress can increase cortisol levels, exacerbating acne.
- Use of inappropriate cosmetics: Comedogenic products can clog pores and worsen the condition.
- Diet: Although controversial, some studies suggest that foods high in sugar and dairy can influence acne.
- Genetic predisposition: People with a family history of acne are more prone to develop it.
- Use of certain medications: Corticosteroids, antidepressants, and some anabolic steroids can aggravate acne.
Types of Acne
Acne can manifest in various forms, the main ones being:- Comedonal Acne: Characterized by open comedones (blackheads) and closed comedones (whiteheads), resulting from pore blockage.
- Inflammatory Acne: Involves red and painful lesions, including papules and pustules (pimples with pus).
- Nodulocystic Acne: A more severe form, with deep, painful nodules and cysts prone to scarring.
- Fulminant Acne: A rare and severe type, with intense inflammation and systemic symptoms such as fever and muscle pain.
- Hormonal Acne: More common in adult women, appearing mainly around the chin and jaw due to hormonal fluctuations.
- Contact Acne: Caused by the use of irritating products or exposure to chemical substances.
Treatments for Acne
Acne treatment varies according to the severity of the condition and may include:- Skin care: Use of specific soaps, non-comedogenic moisturizers, and appropriate sunscreen.
- Salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide: Common ingredients in acne products that help unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
- Topical retinoids: Such as adapalene and tretinoin, which promote cell renewal.
- Topical or oral antibiotics: For moderate to severe cases, they help reduce Propionibacterium acnes bacteria.
- Hormonal contraceptives: For women with hormonal acne, some birth control pills help control sebum production.
- Oral isotretinoin (Roaccutane): Indicated for severe acne, this medication drastically reduces sebum production and combats inflammation. However, it has significant side effects, such as dry skin, liver changes, and mental health risks, requiring careful medical supervision.
- Dermatological treatments: Procedures such as chemical peels, laser therapy, microneedling, and blackhead extraction can assist in acne control.
The Importance of Medical Diagnosis
Self-medication can be dangerous, especially with potent medications like isotretinoin. Each type of acne requires specific treatment, and only a dermatologist can recommend the safest and most effective approach. Inappropriate use of medications can cause severe adverse effects and even worsen acne.Myths and Truths About Acne
There are many popular beliefs about acne, and not all are true. Let’s clarify some of them:- Does chocolate cause acne? – Myth. There is no scientific evidence that chocolate alone causes acne. However, diets high in sugar and dairy may contribute to the problem.
- Does washing the face several times a day help? – Myth. Excessive cleansing can remove the skin’s protective barrier and stimulate more oil production.
- Does sun exposure improve acne? – Myth. Although the sun may temporarily mask lesions, it can cause dryness and increased sebum production, worsening acne in the long run.
- Does makeup worsen acne? – Partially true. The use of comedogenic products can clog pores and aggravate acne, but there are specific makeup products for acne-prone skin that are safe.
- Does squeezing pimples help eliminate them? – Myth. Popping pimples can cause inflammation, infection, and permanent scarring.
How to Prevent Acne?
Some measures help reduce the risk of acne and minimize flare-ups:- Wash your face twice a day: Use gentle products specific to your skin type.
- Avoid squeezing pimples: This can worsen inflammation and cause scarring.
- Choose oil-free cosmetics: Oil-free products help prevent pore blockage.
- Maintain a balanced diet: Avoid excessive ultra-processed and sugary foods.
- Manage stress: Practices like meditation and physical exercise can help.
- Change pillowcases and towels regularly: This prevents the buildup of bacteria and oil on the skin.
- Avoid touching your face constantly: Contact with hands can transfer dirt and oil to the skin.
- Proper hydration: Keeping the skin well hydrated helps balance sebum production.