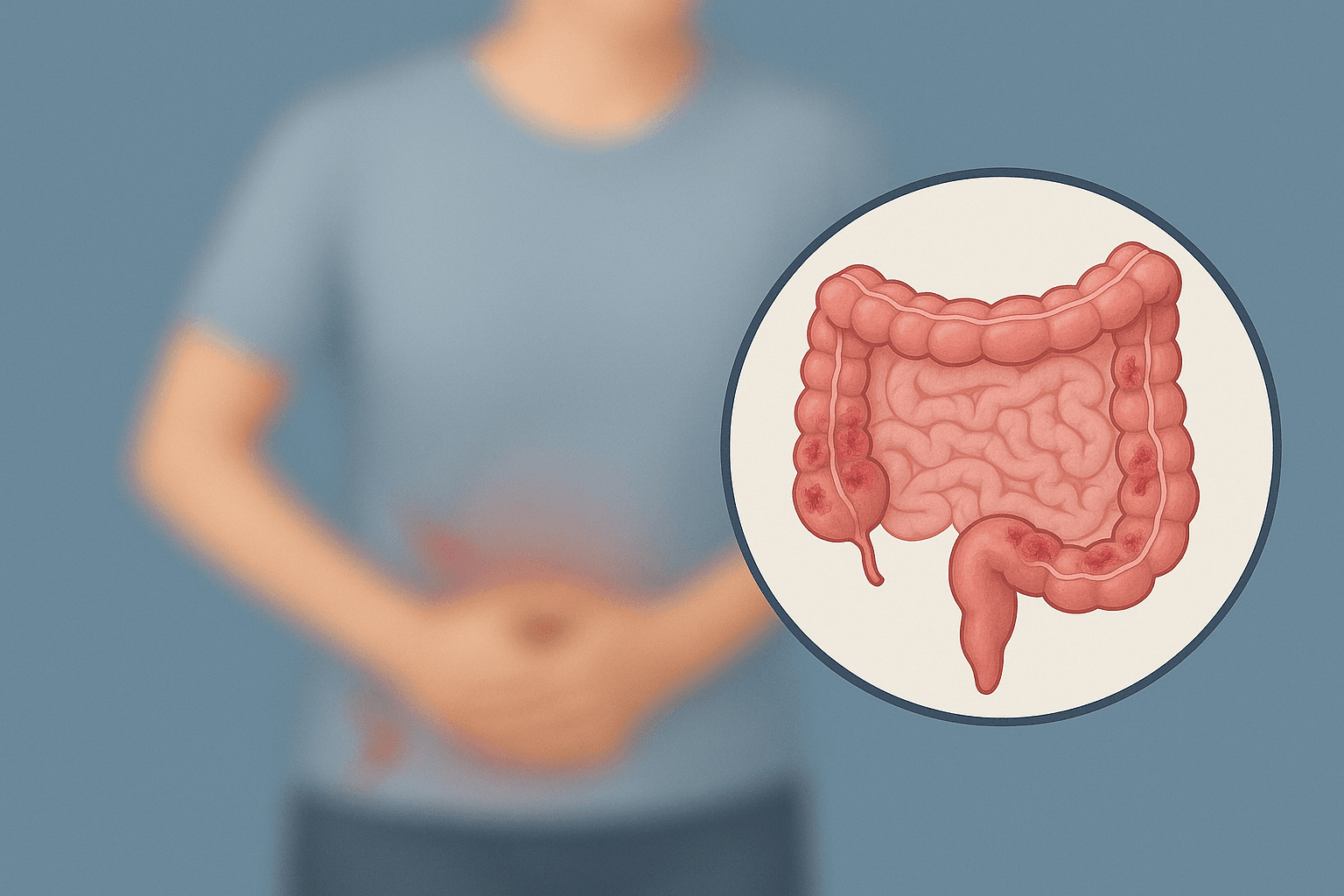
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that primarily affects the colon (large intestine) and rectum. It is characterized by continuous inflammation and the formation of ulcers in the intestinal lining, causing symptoms that can range from mild to severe. Since this is a long-term condition with alternating periods of remission and flare-ups, understanding its signs, causes, and treatments is essential for proper management and improving patients’ quality of life.
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative colitis belongs to the group of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), along with Crohn’s disease. Its main feature is continuous and diffuse inflammation of the colon, usually starting in the rectum and extending to part of or the entire large intestine. Unlike Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, ulcerative colitis is restricted to the colon.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms may vary in intensity and frequency, depending on the extent and severity of inflammation. The most common include:
Persistent diarrhea, often with blood and mucus
Abdominal pain and frequent cramping
Urgency to have a bowel movement, with a sensation of incomplete evacuation
Rectal bleeding, which may lead to anemia
Unintentional weight loss
Severe fatigue, due to chronic inflammation and nutrient loss
In more severe cases, fever, dehydration, and serious complications such as toxic megacolon (a dangerous dilation of the colon) may occur.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is still not fully understood. It is believed to result from a combination of factors:
Autoimmune response: the immune system mistakenly attacks colon cells
Genetic predisposition: family history increases risk
Environmental factors: diet, smoking, and previous intestinal infections may contribute
Contrary to past beliefs, ulcerative colitis is not caused by stress or poor diet, although these factors may worsen symptoms.
Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis
Diagnosis is made through a combination of clinical evaluation, lab tests, and imaging. These may include:
Colonoscopy with biopsy: the most important test to visualize inflammation and collect tissue samples
Blood tests: to detect anemia, inflammation, and specific markers
Stool tests: to rule out infections and check for blood presence
Early diagnosis is important to prevent complications and start appropriate treatment.
Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
The goal of treatment is to control inflammation, reduce symptoms, and maintain remission. Options include:
Intestinal anti-inflammatory drugs: such as mesalamine
Corticosteroids: used in acute flare-ups for rapid inflammation control
Immunosuppressants: to reduce immune system activity
Biologic therapies: modern treatments that block specific inflammatory proteins
Surgery: in severe or treatment-resistant cases, partial or total removal of the colon may be necessary
Additionally, lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and psychological support can help in disease management.
Possible Complications
When not properly treated, ulcerative colitis may lead to serious complications, such as:
Toxic megacolon: severe and potentially life-threatening colon dilation
Intestinal perforation: risk of widespread infection
Increased risk of colon cancer, especially in patients with extensive, long-term inflammation
Because of this, patients with ulcerative colitis should have regular medical follow-ups, including periodic colonoscopies.
Myths, Facts, and Scientific Advances
❌ Myth: Ulcerative colitis is caused by stress.
➝ Fact: Stress may worsen symptoms, but it is not the root cause.❌ Myth: People with ulcerative colitis cannot live a normal life.
➝ Fact: With proper treatment, many patients live normal lives and maintain their daily routines.🧪 Scientific advances: New biologic therapies and targeted medications are transforming treatment, allowing better inflammation control with fewer side effects. In addition, research on the intestinal microbiome is opening new possibilities for future treatments based on personalized probiotics.