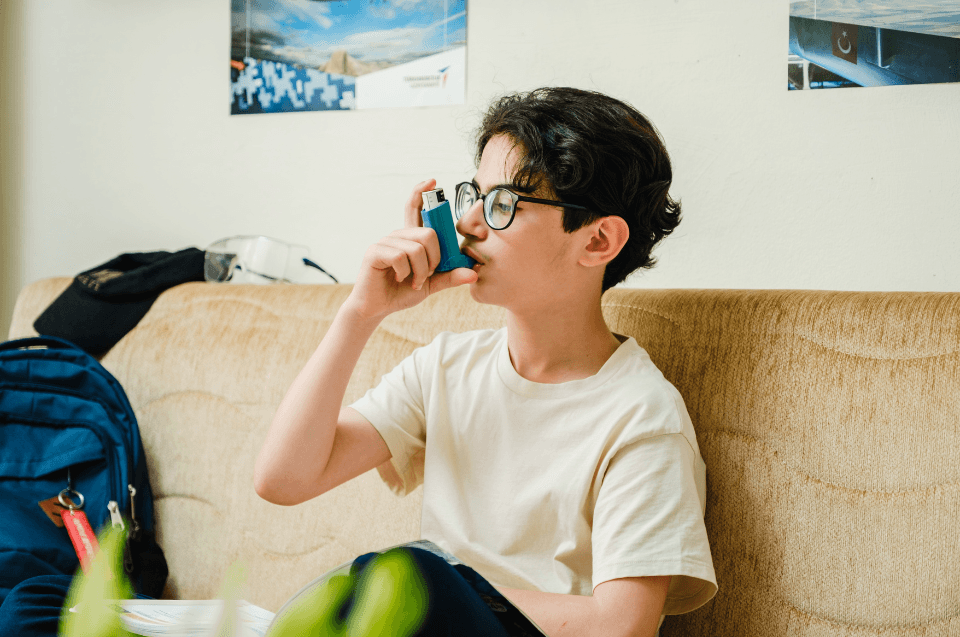
Asthma is one of the most common chronic respiratory diseases worldwide, affecting people of all ages — though it’s more frequently diagnosed in childhood. Characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, asthma can make breathing difficult, trigger episodes of wheezing, and limit daily activities. While there is no cure, asthma can be effectively managed with the right treatment, allowing individuals to live a healthy and active life.
In this article, you’ll learn what asthma is, its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, preventive strategies, and common myths surrounding the condition.
What Is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the bronchi — the tubes that carry air in and out of the lungs. In people with asthma, these airways are persistently inflamed. Certain triggers like dust, pollution, strong odors, or physical activity can cause an exaggerated response, leading the airways to constrict and produce excess mucus.
This combination results in the classic asthma attack: shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness.
What Causes Asthma?
The exact cause of asthma is complex and multifactorial. Rather than a single origin, a combination of genetic and environmental factors contribute to the development of the disease.
Factors associated with asthma include:
Genetic predisposition: Children of parents with asthma are at higher risk.
Allergies: Triggers include dust mites, pollen, pet dander, and mold.
Respiratory infections during childhood: These can impact airway development.
Exposure to smoke and pollutants: Cigarette smoke and air pollution are major risk factors.
Sudden weather changes: Cold air and temperature shifts can provoke symptoms.
Intense physical activity: Especially in cold environments.
What Are the Main Symptoms of Asthma?
Asthma symptoms vary in intensity and frequency. Some individuals may have rare episodes, while others experience frequent or severe attacks.
Most common symptoms include:
Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
Wheezing or whistling sound while breathing
Dry cough, especially at night or early morning
Chest tightness or discomfort
Fatigue after light physical activity
Important: Not all breathing difficulties are caused by asthma. A proper diagnosis must be made by a healthcare professional.
How Is Asthma Diagnosed?
Asthma is diagnosed based on clinical evaluation — the doctor will assess your symptoms and medical history. Additional tests may be recommended:
Spirometry: Measures how much air you can exhale and how quickly.
Bronchial provocation test: Assesses airway sensitivity to specific stimuli.
Allergy tests: Help identify potential environmental triggers.
How Is Asthma Treated?
Although asthma has no definitive cure, it can be controlled effectively with a personalized treatment plan. The goal is to prevent symptoms and allow a normal lifestyle.
Treatment includes:
Bronchodilators: Used during attacks to quickly relieve airway constriction.
Inhaled corticosteroids: Daily medication to control chronic inflammation.
Leukotriene modifiers and biologics: Recommended in moderate to severe cases.
Using an inhaler is safe and essential when prescribed. Improper technique, however, can reduce its effectiveness — always follow medical guidance.
How to Prevent Asthma Attacks
In addition to medication, several strategies help minimize asthma triggers:
Keep indoor spaces clean and free from dust and mold
Avoid exposure to smoke and strong chemical odors
Manage respiratory infections promptly
Use dust-mite-proof bedding
Exercise moderately under medical supervision
Follow your asthma action plan carefully
Asthma Myths and Facts
Asthma is often surrounded by misinformation. Let’s clear up some common myths:
“People with asthma shouldn’t exercise.”
❌ Myth. With proper control, individuals with asthma can — and should — be physically active. Many elite athletes manage asthma successfully.
“Inhalers are harmful.”
❌ Myth. Inhalers are safe and play a critical role in asthma control. The real danger lies in incorrect use or skipping treatment.
“Asthma disappears in adulthood.”
⚠️ Partially true. Some children outgrow asthma, but many continue to experience symptoms into adulthood — though they may become milder.
“Asthma is just an emotional condition.”
❌ Myth. While stress can exacerbate symptoms, asthma is a real inflammatory disease with an immune-based mechanism.
Interesting Facts About Asthma
Asthma affects over 300 million people worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Some fragrances and household cleaners with strong scents can trigger asthma attacks.
With the right treatment, patients can remain symptom-free for years.
Asthma is a leading cause of school and work absenteeism — yet it’s manageable.
Conclusion
Asthma is a serious yet controllable condition. With proper medical guidance, awareness of triggers, and adherence to treatment, individuals can lead full, active lives. Breaking down the myths and focusing on prevention and care is essential to improving quality of life for those living with asthma.