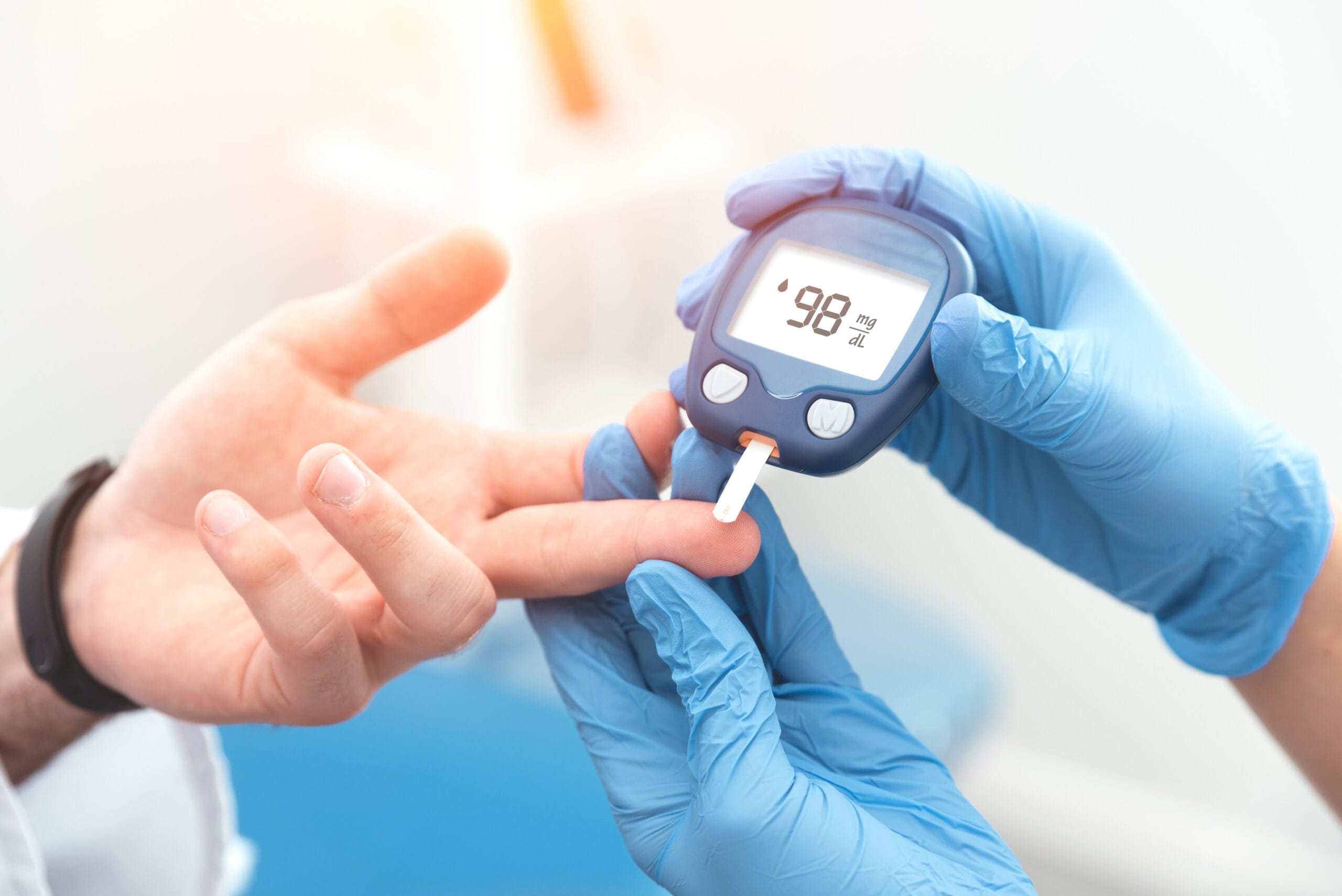
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a metabolic disease characterized by increased blood glucose levels due to problems with insulin production or usage. As the number of cases has grown over the years, understanding the causes of diabetes, its symptoms, and prevention methods is essential for maintaining a healthy life.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus occurs when the body cannot produce insulin properly or when the cells are unable to use it effectively. Insulin is the hormone responsible for allowing blood glucose to enter the cells to be used as energy. When this process doesn’t function correctly, blood sugar levels rise, potentially leading to various diabetes-related complications over time.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
This type is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Usually diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, it requires daily insulin injections to control blood sugar levels.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
The most common form of the disease, type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin. It is often linked to poor lifestyle habits such as unhealthy eating, physical inactivity, and obesity. This type can be managed with lifestyle changes, medication, and insulin if necessary.
3. Gestational Diabetes
This form of diabetes can develop during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that affect insulin function. While many women can manage their blood sugar with diet and exercise, some may require insulin. Gestational diabetes increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
Diabetes Symptoms
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of diabetes, but common signs include:
Excessive thirst
Frequent urination
Intense hunger
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue and extreme tiredness
Blurred vision
Frequent skin or gum infections
Slow-healing wounds
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult an endocrinologist and undergo tests such as fasting blood glucose and A1C (glycated hemoglobin).
Risk Factors
The main risk factors for developing diabetes mellitus include:
Family history of the disease
Being overweight or obese
Sedentary lifestyle
High blood pressure and elevated cholesterol
Diet high in refined carbs and sugars
Advanced age (higher risk for type 2 diabetes)
How to Prevent Diabetes
While type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, type 2 and gestational diabetes can often be avoided through healthy habits:
Maintain a healthy diet: Focus on fiber-rich foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid sugar and ultra-processed foods.
Exercise regularly: Physical activity helps with weight control and improves insulin sensitivity.
Keep a healthy weight: Overweight and obesity are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Manage stress: Chronic stress can lead to elevated blood glucose levels.
Have regular check-ups: Monitoring blood sugar levels can help detect issues early and prevent complications.
Complications of Diabetes
If not properly controlled, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as:
Cardiovascular disease
Kidney failure
Vision problems, including blindness
Diabetic neuropathy, causing pain and loss of sensation in limbs
Diabetic foot, which can result in amputations
Proper diabetes management is essential to prevent severe health consequences.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a chronic disease, but with proper care, it’s possible to live well and with good quality of life. Healthy eating, regular physical activity, and consistent medical monitoring are key to both preventing and managing diabetes. If you have a family history or risk factors, adopt healthy habits and stay alert to the symptoms of diabetes.
If this article was helpful to you, share it with your friends and family so more people can better understand this condition and learn how to prevent diabetes!